CMMS Meaning
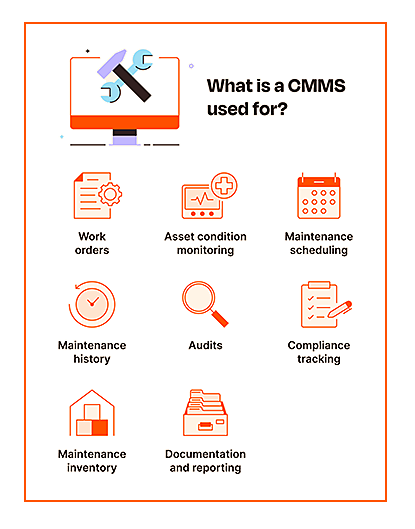
CMMS software is a computer-based application that helps organizations manage and maintain their assets, equipment, and facilities more efficiently. It is designed to streamline, automate maintenance operations, planning, scheduling, tracking and reporting

CMMS Meaning
-
CMMS stands for Computerized Maintenance Management System. CMMS software is a computer-based application that helps organizations manage and maintain their assets, equipment, and facilities more efficiently. It is designed to streamline and automate maintenance operations, including planning, scheduling, tracking, and reporting.
Panther CMMS software for example typically offers a range of features and functionalities that assist maintenance teams in effectively managing their work. Some common features include:
Asset Management: CMMS software allows organizations to create a centralized database of all their assets, including equipment, machinery, vehicles, and facilities. It tracks relevant information such as maintenance history, specifications, warranties, and locations.
Preventive Maintenance: Panther CMMS enables the scheduling and management of preventive maintenance tasks. It can generate work orders and reminders for routine inspections, servicing, and replacements to minimize breakdowns and extend the lifespan of assets.
Work Order Management: Panther CMMS software helps manage work orders throughout their lifecycle. It allows users to create, assign, and prioritize work orders, track progress, allocate resources, and document completed tasks. Facilitate communication between maintenance and supervisors.
Inventory and Parts Management: CMMS software often includes inventory management capabilities, allowing users to track spare parts, consumables, and materials needed for maintenance activities.
Reporting and Analytics: Panther CMMS software generates various reports and performance metrics to provide insights into maintenance operations. It can produce maintenance histories, cost analysis, asset performance data, and other relevant reports to aid decision-making and optimize maintenance strategies.
Mobile Accessibility: Panther CMMS solution offers mobile applications or responsive interfaces, enabling maintenance technicians to access the system from smartphones or tablets. This allows them to view work orders, update task statuses, access asset information, and capture data in real-time while working in the field.
Panther CMMS software offers numerous benefits, such as improved asset reliability, reduced downtime, increased maintenance efficiency, better resource allocation, and enhanced regulatory compliance. It helps organizations streamline maintenance processes, extend asset lifespan, and optimize their maintenance strategies to improve overall operational efficiency.
Why is CMMS important to use
CMMS (Computerized Maintenance Management System) is important to use for several reasons, especially in industries and organizations where maintenance of assets, equipment, and facilities is crucial. Here are some key reasons why CMMS is important:
Organizes Maintenance Operations: CMMS helps in organizing and centralizing all maintenance-related information, such as equipment data, maintenance schedules, work orders, and historical maintenance records. This streamlines maintenance processes and ensures that maintenance tasks are efficiently managed.
Preventive Maintenance: CMMS enables the implementation of preventive maintenance strategies. By scheduling routine maintenance tasks, inspections, and replacements, potential issues can be identified and resolved before they turn into major problems. This reduces downtime, extends the life of assets, and prevents costly breakdowns.
Improved Asset Management: CMMS provides insights into the health and performance of assets. It tracks asset history, maintenance costs, and usage patterns, allowing organizations to make informed decisions about repair, replacement, or upgrades.
Resource Planning and Allocation: CMMS helps in planning and allocating resources more effectively. It assists in determining the required manpower, spare parts, and tools necessary for specific maintenance tasks, optimizing resource utilization and reducing wastage.
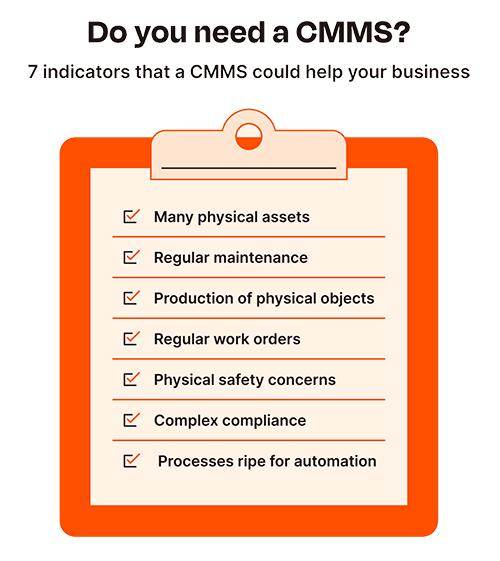 Work Order Management: CMMS streamlines the process of creating, assigning, and tracking work orders. This ensures that maintenance tasks are completed promptly, and there is clear accountability for each task.
Work Order Management: CMMS streamlines the process of creating, assigning, and tracking work orders. This ensures that maintenance tasks are completed promptly, and there is clear accountability for each task.
Data-Driven Decision Making: With CMMS, organizations can access valuable data and reports on maintenance performance, downtime, costs, and other key metrics. This data-driven approach allows for continuous improvement of maintenance strategies and operational efficiency.
Regulatory Compliance: In certain industries, compliance with regulations and safety standards is crucial. CMMS helps organizations maintain compliance by tracking and documenting maintenance activities, inspections, and certifications.
Cost Savings: Implementing CMMS can lead to significant cost savings in the long run. By optimizing maintenance schedules, reducing equipment downtime, and avoiding costly emergency repairs, organizations can cut down on maintenance expenses.
Increased Productivity: With streamlined maintenance processes and quick access to information, maintenance teams can become more productive and responsive to issues, leading to increased overall productivity.
Enhanced Safety: Properly maintained equipment and facilities contribute to a safer working environment for employees, reducing the risk of accidents and injuries.
Panther CMMS (Computerized Maintenance Management System) is a software solution designed to help organizations manage their maintenance operations more efficiently and effectively. It is a comprehensive tool that streamlines maintenance processes, including work order management, asset tracking, inventory management, preventive maintenance scheduling, and reporting.
The primary goal of Panther CMMS is to help organizations minimize equipment downtime, reduce maintenance costs, and improve overall equipment reliability. It provides a centralized platform for managing maintenance operations, enabling maintenance teams to streamline processes, increase productivity, and enhance collaboration. Features of Panther CMMS include:
- Work order management: The system allows maintenance teams to create, assign, and track work orders, as well as manage associated tasks, parts, and labor.
- Asset tracking: Panther CMMS enables organizations to track the location, maintenance history, and performance of their assets.
- Preventive maintenance scheduling: The system allows maintenance teams to schedule and manage preventive maintenance tasks, ensuring that assets are properly maintained and reducing the likelihood of unscheduled downtime.
- Inventory management: Panther CMMS provides inventory tracking and management, enabling organizations to maintain sufficient inventory levels and optimize inventory costs.
- Reporting and analytics: The system provides a range of customizable reports and analytics, enabling organizations to gain insights into maintenance operations and make data-driven decisions.
- Mobile accessibility: Panther CMMS is accessible from mobile devices, allowing maintenance teams to manage work orders and access critical information on the go.
Panther CMMS is designed to be flexible and scalable, making it suitable for organizations of all sizes and industries. It is a valuable tool for maintenance teams looking to improve their efficiency, reduce costs, and optimize their operations.In conclusion, CMMS is important to use because it helps organizations improve maintenance efficiency, extend asset life, reduce downtime, make data-driven decisions, and ultimately achieve cost savings and improved productivity. It plays a vital role in managing maintenance operations, which is crucial for the smooth functioning of many industries and organizations.
Work Order Management Software
-
Work order management software is a computer-based tool designed to facilitate and streamline the process of managing work orders within an organization. It provides a centralized platform to create, assign, track, and complete work orders efficiently. Work orders typically represent specific tasks or jobs that need to be completed, such as maintenance, repairs, installations, inspections, or any other type of work requiring coordination and documentation.
Work order management software offers several features and functionalities to support the entire lifecycle of a work order. Here are some key aspects:
Creation and Assignment: The software allows users to create new work orders by providing details such as the task description, priority, location, required resources, and any associated documentation or instructions. Work orders can be assigned to specific individuals, teams, or departments responsible for completing the task.
Tracking and Status Updates: Work order management software enables real-time tracking of work orders. It provides visibility into the status of each work order, including its progress, current stage, and any associated notes or comments. This helps supervisors and stakeholders stay informed about ongoing tasks.
Scheduling and Prioritization: Panther CMMS helps in scheduling and prioritizing work orders based on factors such as urgency, available resources, and dependencies. It allows users to set due dates, assign deadlines, and adjust priorities as needed. This ensures that critical tasks are addressed promptly and efficiently.
Resource Allocation: Work order management software helps in managing and allocating resources required to complete work orders. It allows users to assign specific personnel, equipment, tools, and materials to each task. This ensures that the necessary resources are available and assigned appropriately to maximize efficiency.
Communication and Collaboration: Panther CMMS software facilitates communication and collaboration between team members, supervisors, and other stakeholders involved in the work order process. It enables the exchange of messages, notifications, and updates within the platform, reducing reliance on manual communication channels.
Documentation and Reporting: Work order management software allows for the documentation and storage of relevant information associated with work orders. It enables users to attach files, images, manuals, or any other supporting documents. The software also generates reports and analytics on work order performance, task completion rates, and other metrics to aid in decision-making and process improvement.
Panther CMMS, work order management software enhances organizational efficiency by providing a structured approach to creating, assigning, tracking, and completing work orders. It improves communication, resource allocation, and visibility, resulting in better task management and overall productivity.
Why is Work Order Management Software important to use
Work Order Management Software (WOMS) is important to use for organizations that deal with maintenance, service, or project-based work. It provides a digital platform to streamline and optimize work order processes. Here are some key reasons why WOMS is important:
Centralized Work Order System: WOMS allows organizations to have a centralized and accessible system for creating, managing, and tracking work orders. This eliminates the need for manual paperwork, reduces the chances of lost or misplaced orders, and improves overall efficiency.
Real-Time Visibility: With WOMS, supervisors and team members can have real-time visibility into the status of work orders. This helps in better coordination, scheduling, and allocation of resources, leading to faster completion of tasks.
Improved Communication: WOMS facilitates seamless communication between different stakeholders involved in the work order process. Technicians can receive work orders directly on their mobile devices, and they can provide updates, add notes, or request additional information in real-time.
Prioritization and Scheduling: Work Order Management Software allows organizations to prioritize and schedule work orders based on urgency, importance, available resources, and other factors. This ensures that critical tasks are addressed promptly and that resources are utilized efficiently.
Preventive Maintenance Planning: WOMS enables the implementation of preventive maintenance strategies by automating the scheduling of routine inspections and maintenance tasks. This helps in identifying and addressing potential issues before they escalate, leading to cost savings and improved asset longevity.
Data Collection and Analysis: WOMS collects data on work order history, completion times, resource usage, and other metrics. This data can be analyzed to identify trends, bottlenecks, and opportunities for process improvement.
Documentation and Compliance: WOMS helps in maintaining a comprehensive digital record of all work orders, including the tasks performed, materials used, and time taken. This documentation is valuable for compliance purposes, audits, and regulatory requirements.
Customer Satisfaction: WOMS can enhance customer satisfaction by providing transparency and timely updates on the progress of work orders. Clients can be notified when a task is completed, which helps in building trust and maintaining good relationships.
Resource Management: WOMS allows organizations to manage their resources effectively. It helps in tracking the availability and utilization of equipment, materials, and personnel, preventing overbooking or underutilization of resources.
Cost Control: By optimizing work order processes and reducing downtime, WOMS can lead to cost savings for organizations. It helps in identifying inefficiencies and areas where improvements can be made to reduce operational expenses.
In summary, Work Order Management Software is important to use because it streamlines work order processes, improves communication and visibility, enables preventive maintenance planning, enhances resource management, and contributes to better customer satisfaction. The data-driven insights provided by WOMS help organizations make informed decisions, achieve cost savings, and increase overall operational efficiency.
Preventative Maintenance
-
Panther CMMS Preventive maintenance software, also known as PM software or preventive maintenance management software, is a computer-based tool designed to help organizations implement and manage preventive maintenance programs for their assets, equipment, and facilities. Preventive maintenance aims to reduce the likelihood of unexpected breakdowns, extend asset lifespan, and improve overall operational efficiency by conducting regular inspections, servicing, and replacements based on predefined schedules or condition-based triggers.
Preventive maintenance software offers a range of features and functionalities to support the planning, execution, and management of preventive maintenance activities. Here are some key aspects:
Scheduling and Planning: The software allows users to schedule preventive maintenance tasks based on time-based intervals (e.g., monthly, quarterly, annually) or condition-based triggers (e.g., meter readings, sensor data). It provides a centralized calendar or scheduler to view and manage upcoming maintenance activities.
Task Creation and Assignment: Preventive maintenance software enables users to create and define specific maintenance tasks, including detailed instructions, checklists, required resources, and estimated durations. Tasks can be assigned to individuals or teams responsible for performing the maintenance activities.
Work Order Generation: The software can automatically generate work orders for preventive maintenance tasks. Work orders include relevant information such as task details, asset information, due dates, assigned personnel, and any associated documentation. This helps streamline the execution and tracking of preventive maintenance activities.
Task Tracking and Completion: Preventive maintenance software allows users to track the progress of preventive maintenance tasks in real-time. It provides visibility into task statuses, completion dates, and any notes or comments associated with each task. This helps monitor compliance and identify any outstanding or overdue tasks.
Asset History and Documentation: The software maintains a centralized database of assets and their maintenance histories. It records maintenance activities, including dates, tasks performed, parts replaced, and any associated costs. This historical data helps track asset performance, identify recurring issues, and support warranty claims or audits.
Notifications and Reminders: Preventive maintenance software sends notifications and reminders to maintenance personnel, supervisors, or other stakeholders to ensure timely execution of preventive maintenance tasks. These notifications can be delivered via email, SMS, or within the software itself, helping to prevent missed or delayed maintenance activities.
Reporting and Analytics: The software generates reports and analytics on preventive maintenance performance. It provides insights into completion rates, asset downtime, costs, and other key metrics. These reports aid in assessing the effectiveness of the preventive maintenance program and making data-driven decisions for process improvements.
By utilizing preventive maintenance software, organizations can proactively manage their assets, reduce unplanned downtime, increase equipment reliability, and optimize maintenance resources and costs. It helps implement structured preventive maintenance programs, ensuring that assets are regularly inspected, serviced, and maintained to minimize failures and maximize operational efficiency.
Why is Preventative Maintenance Software important to use
Preventive Maintenance Software (PMS) is important to use for organizations that rely on equipment, machinery, and assets to carry out their operations. PMS automates and optimizes preventive maintenance processes, ensuring that equipment is regularly inspected, serviced, and maintained. Here are some key reasons why Preventive Maintenance Software is important:
Increased Equipment Reliability: PMS helps in identifying and addressing potential issues before they cause equipment failures or breakdowns. By conducting regular inspections and maintenance, the software ensures that equipment remains in good working condition, leading to increased reliability and reduced downtime.
Extended Asset Lifespan: Regular maintenance and timely repairs provided by PMS contribute to extending the lifespan of equipment and assets. This means that organizations can maximize their return on investment (ROI) by using their assets for a longer period.
Cost Savings: Preventive maintenance is generally less expensive than corrective or emergency maintenance. PMS enables organizations to plan maintenance tasks efficiently, schedule them during periods of low production, and avoid costly unplanned breakdowns.
Improved Safety: Well-maintained equipment is safer to operate, reducing the risk of accidents and injuries in the workplace. PMS ensures that safety-critical components are regularly inspected and replaced as needed, providing a safer working environment for employees.
Regulatory Compliance: In many industries, there are strict regulations and standards that organizations must adhere to. PMS helps organizations stay compliant by automatically scheduling and documenting maintenance activities, inspections, and certifications.
Better Planning and Resource Management: PMS provides a structured approach to maintenance planning. It helps in allocating the right resources, such as labor, spare parts, and tools, at the right time, ensuring that maintenance tasks are performed efficiently.
Reduced Reactive Maintenance: Reactive maintenance, addressing issues only when they occur, can be costly and disruptive. PMS reduces the need for reactive maintenance by proactively addressing potential problems, leading to smoother operations.
Data-Driven Decision Making: PMS generates valuable data and reports on equipment performance, maintenance history, and costs. This data-driven approach allows organizations to make informed decisions about equipment replacement, upgrades, or changes to maintenance strategies.
Increased Productivity: With PMS in place, maintenance teams can focus on planned maintenance tasks rather than reacting to unexpected breakdowns. This leads to increased productivity and more efficient use of labor resources.
Enhanced Asset Management: PMS provides a comprehensive view of all assets and their maintenance history. This information helps organizations make informed decisions about asset utilization, retirement, or replacement.
In conclusion, Preventive Maintenance Software is important to use because it optimizes maintenance processes, increases equipment reliability, extends asset lifespan, reduces downtime, ensures regulatory compliance, and contributes to cost savings. By implementing preventive maintenance strategies with the help of PMS, organizations can operate more efficiently, reduce risks, and make data-driven decisions to improve overall performance.
Asset Management Software
-
Panther CMMS Asset management software, also known as asset tracking software or asset management system, is a computer-based tool that helps organizations track, monitor, and manage their physical assets throughout their lifecycle. Assets can include equipment, machinery, vehicles, facilities, IT hardware, furniture, or any other valuable items that play a role in the organization's operations.
Asset management software offers a range of features and functionalities to streamline asset management processes. Here are some key aspects:
Asset Tracking and Identification: The software provides a centralized database to record and track information about each asset. It includes details such as asset names, descriptions, serial numbers, purchase dates, warranty information, locations, and custodians. It may also support barcode or RFID scanning to facilitate quick and accurate asset identification.
Asset Lifecycle Management: Asset management software helps manage assets throughout their lifecycle, from acquisition to disposal. It allows users to record information about procurement, maintenance history, repairs, upgrades, and retirement of assets. This enables organizations to make informed decisions regarding asset utilization, replacement, and retirement planning.
Maintenance and Service Management: The software can integrate with maintenance and service management modules to schedule and track maintenance activities related to assets. It helps generate work orders, track maintenance history, and schedule preventive maintenance tasks. This ensures assets are properly maintained, reducing downtime and extending their lifespan.
Location and Movement Tracking: Asset management software enables tracking the physical location and movement of assets. It can capture information about asset transfers between departments, sites, or employees. This helps organizations optimize asset utilization, prevent loss or theft, and facilitate inventory audits.
Depreciation and Financial Management: The software may include features for tracking asset depreciation, value, and financial information. It assists in calculating depreciation schedules, tracking asset values over time, and generating financial reports related to asset investments, costs, and valuation.
Reporting and Analytics: Asset management software generates reports and analytics on asset-related data. It provides insights into asset utilization, maintenance costs, depreciation, compliance, and other key metrics. These reports help organizations make data-driven decisions, optimize asset allocation, and improve overall asset management strategies.
Integration and Scalability: Asset management software may offer integration capabilities with other systems, such as procurement systems, financial management software, or enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems. This allows for seamless data flow and streamlines asset-related processes across different departments. Additionally, the software should be scalable to accommodate a growing asset inventory and organizational needs.
Panther CMMS Asset management software provides organizations with a centralized platform to efficiently track, manage, and optimize their assets. It enhances asset visibility, improves maintenance planning, reduces costs, and maximizes asset utilization. By implementing asset management software, organizations can make informed decisions, streamline processes, and enhance overall asset lifecycle management.
Is Asset Management Software important?
Asset Management Software (AMS) is crucial for organizations that possess and rely on a wide range of assets, such as equipment, machinery, facilities, vehicles, IT hardware, and more. Here are some key reasons why Asset Management Software is important to use:
 Centralized Asset Information: AMS provides a centralized repository for all asset-related information, including asset details, maintenance history, warranty information, location, and more. Having this information readily accessible and organized streamlines asset management processes.
Centralized Asset Information: AMS provides a centralized repository for all asset-related information, including asset details, maintenance history, warranty information, location, and more. Having this information readily accessible and organized streamlines asset management processes.
 Improved Asset Tracking: Asset Management Software enables organizations to track the location, condition, and status of their assets in real-time. This reduces the risk of asset loss, theft, or misplacement and allows for better utilization of assets.
Improved Asset Tracking: Asset Management Software enables organizations to track the location, condition, and status of their assets in real-time. This reduces the risk of asset loss, theft, or misplacement and allows for better utilization of assets.
Optimized Asset Utilization: By having a clear view of asset availability and usage patterns, organizations can optimize asset utilization. This prevents overutilization of certain assets while identifying opportunities to reallocate or share assets when they are underutilized.
Enhanced Maintenance Planning: AMS integrates asset maintenance data, allowing for better planning of preventive maintenance and inspections. This proactive approach reduces downtime, extends asset life, and prevents costly breakdowns.
Regulatory Compliance: In industries with specific regulations and standards, AMS helps in managing assets to ensure compliance. It enables organizations to track and document asset-related activities, certifications, and inspections.
Cost Management: Asset Management Software provides insights into asset-related costs, including acquisition, maintenance, and disposal expenses. This information allows organizations to identify cost-saving opportunities and make informed decisions about asset investments.
Asset Lifecycle Management: AMS supports the entire asset lifecycle, from acquisition to disposal. It helps organizations make informed decisions about when to retire or replace assets, considering factors like maintenance costs and depreciation.
Risk Mitigation: Effective asset management reduces operational risks. With AMS, organizations can identify potential risks associated with assets, such as safety hazards or compliance issues, and take appropriate actions to mitigate those risks.
Efficient Procurement and Vendor Management: Asset Management Software can assist in the procurement process by providing data on asset performance and maintenance costs. This helps organizations make better decisions when purchasing new assets and managing vendor relationships.
Data-Driven Decision Making: AMS generates valuable data and analytics related to assets. This data-driven approach allows organizations to make strategic decisions, plan for future needs, and optimize asset-related processes.
Simplified Audits and Reporting: AMS facilitates asset audits and generates comprehensive reports on asset performance, maintenance history, and compliance status. This simplifies the auditing process and ensures accurate and up-to-date records.
In conclusion, Asset Management Software is essential for organizations to effectively manage their assets throughout their lifecycle. It improves asset tracking, utilization, maintenance planning, compliance, and cost management. By using AMS, organizations can optimize asset performance, reduce risks, and make data-driven decisions to improve overall efficiency and productivity.
Inventory Management Software
-
Panther CMMS Inventory management software is a computer-based tool designed to help organizations efficiently manage their inventory of products, materials, or supplies. It provides a centralized platform to track, monitor, and control inventory levels, ensuring optimal stock availability while minimizing costs and inventory-related risks.
Inventory management software offers various features and functionalities to streamline inventory operations. Here are some key aspects:
Inventory Tracking: Panther CMMS allows organizations to maintain a real-time record of their inventory. It tracks item names, descriptions, quantities, locations, unit costs, and other relevant details. It provides visibility into stock levels, ensuring accurate inventory tracking and reducing the risk of stockouts or overstocking.
Order Management: Inventory management software facilitates the management of purchase orders and sales orders. It enables users to create and track orders, monitor order statuses, and generate purchase or sales reports. This helps organizations maintain an optimal balance between supply and demand.
Replenishment and Restocking: The software assists in managing inventory replenishment. It uses historical data and demand forecasting algorithms to determine optimal reorder points, reorder quantities, and lead times. It generates automated alerts or purchase orders when stock levels fall below predefined thresholds.
Barcode or RFID Integration: Inventory management software often integrates with barcode or RFID scanning technologies. This allows for efficient and accurate data capture during inventory receiving, picking, and stock counting processes. It improves inventory visibility, reduces errors, and speeds up inventory-related tasks.
Warehouse Management: Some inventory management software includes warehouse management features. It helps organizations optimize warehouse layout, manage bin locations, and track inventory movements within the warehouse. This streamlines picking, packing, and fulfillment processes.
Reporting and Analytics: Inventory management software generates reports and analytics on inventory-related data. It provides insights into inventory turnover rates, stock valuation, obsolete or slow-moving items, and other key metrics. These reports assist in inventory optimization, identifying trends, and making data-driven decisions.
Integration and Scalability: Inventory management software may offer integration capabilities with other systems, such as accounting software, point-of-sale (POS) systems, or e-commerce platforms. This enables seamless data synchronization and streamlines inventory-related processes across different departments. The software should also be scalable to accommodate changing inventory volumes and organizational needs.
By utilizing Panther CMMS inventory management software, organizations can streamline their inventory operations, reduce carrying costs, minimize stockouts, and optimize stock levels. It improves inventory accuracy, enhances order fulfillment, and provides valuable insights for effective inventory planning and decision-making.
Why is Inventory Management Software important to use
Inventory Management Software (IMS) is essential for businesses that handle inventory, whether it's raw materials, finished goods, or any other type of product. Here are some key reasons why Inventory Management Software is important to use:
Real-Time Inventory Tracking: IMS provides real-time visibility into inventory levels, locations, and movements. This helps businesses accurately track stock levels and avoid stockouts or overstock situations, leading to better inventory control.
Improved Order Fulfillment: With IMS, businesses can efficiently manage incoming orders and ensure that they have the right amount of stock available to meet customer demands. This reduces order processing times and improves customer satisfaction.
Cost Savings: By optimizing inventory levels and reducing excess stock, IMS helps businesses save on carrying costs, storage expenses, and potential losses due to expired or obsolete inventory.
Automated Reordering: Inventory Management Software can automatically generate purchase orders or replenishment requests when stock levels fall below predetermined thresholds. This streamlines the reordering process and minimizes manual intervention.
Enhanced Accuracy: IMS reduces the likelihood of errors in inventory management. Automation minimizes manual data entry errors, and barcode or RFID technology can be used to ensure accurate tracking of inventory movements.
Inventory Forecasting: Inventory Management Software often comes with forecasting features, allowing businesses to predict demand and plan inventory levels accordingly. This aids in better inventory planning and reduces the risk of stockouts or overstocking.
Optimized Warehouse Management: IMS helps in organizing inventory within the warehouse efficiently. It provides insights into storage space availability and optimal placement of items, making the most of the warehouse's capacity.
Integration with Sales and Accounting: Many IMS solutions integrate with other business systems, such as sales and accounting software. This seamless integration ensures that inventory data is synchronized across departments, reducing duplication of efforts and ensuring accurate financial reporting.
Efficient Returns Management: Inventory Management Software streamlines the handling of returns and helps businesses track returned items, process refunds or replacements, and manage inventory adjustments effectively.
Compliance and Auditing: IMS assists in maintaining accurate inventory records, making it easier for businesses to comply with regulatory requirements and pass audits with confidence.
Data-Driven Decision Making: By providing comprehensive inventory data and analytics, IMS enables data-driven decision-making. Businesses can identify trends, optimize inventory strategies, and make informed choices about purchasing and pricing.
Scalability: As businesses grow, managing inventory becomes more complex. IMS scales to accommodate the growing inventory needs of the business, ensuring continued efficiency in inventory management.
In conclusion, Inventory Management Software is crucial for businesses to streamline inventory operations, optimize stock levels, reduce costs, improve order fulfillment, and make data-driven decisions. By using IMS, businesses can enhance their overall inventory control, leading to increased productivity and profitability.
Purchase Order Software
-
Panther CMMS Purchase order software, also known as PO software, is a computer-based tool designed to automate and streamline the process of creating, managing, and tracking purchase orders within an organization. Purchase orders are documents issued by a buyer to a supplier, outlining the details of the requested products or services, quantities, prices, delivery dates, and terms of purchase.
Purchase order software offers several features and functionalities to simplify the procurement process. Here are some key aspects:
1. Purchase Order Creation: Panther CMMS allows users to create purchase orders electronically. It provides templates or forms where users can input the necessary information, including the supplier details, item descriptions, quantities, prices, and any other relevant terms or instructions. This eliminates the need for manual paperwork and ensures consistent formatting.
2. Approval Workflow: Purchase order software often includes an approval workflow feature. It allows users to route purchase orders to the appropriate personnel or departments for review and approval. It can be configured to follow predefined rules or hierarchies, ensuring proper authorization before proceeding with the purchase.
3. Supplier Management: Panther CMMS helps manage supplier information and relationships. It maintains a centralized database of supplier details, including contact information, payment terms, lead times, and performance ratings. This helps users select the appropriate supplier for each purchase order and facilitates communication with suppliers.
4. Budget and Cost Control: Purchase order software allows users to set budget limits and control spending. It provides visibility into available budgets and alerts users if a purchase order exceeds the allocated funds. This helps prevent overspending and promotes financial accountability.
5. Integration with Inventory Management: Some purchase order software integrates with inventory management or warehouse management systems. This enables real-time inventory visibility, allowing users to determine stock availability and avoid overordering. It can also trigger automatic inventory updates based on purchase orders received.
6. Tracking and Notifications: Purchase order software enables users to track the status of purchase orders throughout the procurement process. It provides real-time updates on order approvals, shipment status, and delivery dates. Users can also receive notifications or alerts for critical events, such as delayed deliveries or changes to order details.
7. Reporting and Analytics: Purchase order software generates reports and analytics related to purchase orders. It provides insights into spending patterns, supplier performance, lead times, and other key metrics. These reports assist in analyzing purchasing trends, identifying cost-saving opportunities, and optimizing procurement strategies.
By utilizing Panther CMMS purchase order software, organizations can streamline their procurement processes, reduce manual errors, enhance communication with suppliers, and improve financial control. It increases efficiency, reduces administrative tasks, and provides better visibility into purchasing activities for effective decision-making.
Why is Purchase Order Software important to use
Purchase Order Software (POS) is essential for businesses to streamline and automate their procurement processes. It facilitates the creation, approval, tracking, and management of purchase orders, providing several important benefits. Here are some key reasons why Purchase Order Software is important to use:
Efficient Procurement Process: POS simplifies the procurement process by automating the creation of purchase orders. It ensures that the correct items are ordered, at the right quantities, from approved suppliers, reducing errors and delays.
Saves Time and Reduces Paperwork: With POS, purchase orders can be generated electronically, eliminating the need for manual paperwork and reducing administrative burden. This saves time and allows employees to focus on more strategic tasks.
Real-Time Visibility: Purchase Order Software provides real-time visibility into the status of purchase orders. This enables stakeholders to track the progress of orders, from creation to delivery, ensuring better coordination and timely receipt of goods or services.
Accurate Order Tracking: POS helps in accurately tracking orders, ensuring that items are received as expected and that vendors meet their commitments. This reduces discrepancies and disputes with suppliers.
Budget Control: POS allows businesses to set budget limits and spending thresholds for each purchase. It ensures that purchases align with the budgetary constraints, preventing overspending and promoting cost control.
Approval Workflows: Purchase Order Software often includes customizable approval workflows. This ensures that all purchase orders go through the appropriate channels for approval, enhancing control and compliance.
Vendor Management: POS centralizes vendor information and performance data. This helps businesses make informed decisions about which vendors to work with based on past performance, pricing, and reliability.
Compliance and Audit Trail: Purchase Order Software maintains a detailed audit trail of all purchasing activities. This is valuable for compliance purposes, internal audits, and external regulatory requirements.
Integration with Accounting and Inventory: POS can integrate with accounting and inventory management systems, streamlining data flow and reducing the need for manual data entry.
Improved Supplier Relationships: By streamlining the procurement process and ensuring timely payments, POS helps in building stronger relationships with suppliers, leading to better terms, discounts, and improved service.
Data-Driven Decision Making: Purchase Order Software provides data and analytics on purchasing trends, supplier performance, and spending patterns. This enables data-driven decision-making and cost optimization.
Scalability: As businesses grow, the volume of purchase orders can increase significantly. POS is designed to handle larger procurement needs, ensuring that the software can scale with the organization's growth.
In conclusion, Purchase Order Software is essential for businesses to manage their procurement processes efficiently. It saves time, reduces paperwork, provides real-time visibility, enhances budget control, and fosters better supplier relationships. By using POS, businesses can improve their procurement efficiency, reduce costs, and make informed decisions to optimize their purchasing operations.
Machine Learning CMMMS
-
Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) software is used to manage and optimize maintenance activities within an organization. Machine learning can enhance CMMS software in several ways, making maintenance processes more efficient, predictive, and cost-effective. Here's how machine learning helps with CMMS software:
1. Predictive Maintenance: Machine learning algorithms can analyze historical maintenance data, equipment performance metrics, and sensor data to predict when equipment is likely to fail. By identifying patterns and trends, ML algorithms can help in predicting maintenance needs before a breakdown occurs. This minimizes downtime, reduces maintenance costs, and extends the lifespan of machinery.
2. Optimized Work Scheduling: Machine learning algorithms can optimize work order schedules by considering various factors such as equipment availability, technician skills, historical performance data, and priority levels. This ensures that maintenance tasks are scheduled efficiently, reducing idle time and maximizing productivity.
3. Anomaly Detection: ML algorithms can detect anomalies in equipment behavior or performance. Sudden deviations from normal operating conditions can trigger alerts, indicating potential issues. Maintenance teams can then investigate these anomalies promptly, preventing major breakdowns and costly repairs.
4. Inventory Management: Machine learning can analyze usage patterns and forecast demand for spare parts and inventory items. By predicting which parts are likely to be needed and when, organizations can maintain optimal inventory levels, reducing carrying costs while ensuring that necessary parts are always available when required.
5. Energy Management: ML algorithms can analyze energy consumption patterns and identify opportunities for energy savings. By optimizing equipment usage and scheduling maintenance tasks during off-peak energy hours, organizations can reduce energy costs and promote sustainability.
6. Root Cause Analysis: When equipment failures occur, machine learning can assist in analyzing various data sources to identify root causes. By understanding why failures happen, organizations can take proactive measures to prevent similar issues in the future.
7. Natural Language Processing (NLP) for Data Input: NLP can be integrated into CMMS software to allow users to input data using natural language. This simplifies the process of logging maintenance requests, updating work orders, and extracting insights from textual data, making the software more user-friendly.
8. Continuous Improvement: Machine learning algorithms can analyze maintenance data to provide insights into the effectiveness of maintenance strategies. By identifying what works and what doesn’t, organizations can continuously improve their maintenance processes, leading to better operational efficiency and cost savings over time.
In summary, machine learning enhances CMMS software by enabling predictive maintenance, optimizing scheduling, detecting anomalies, improving inventory management, managing energy usage, facilitating root cause analysis, enabling natural language interactions, and supporting continuous improvement efforts. These capabilities collectively result in more efficient maintenance processes, reduced downtime, and cost savings for organizations.
Machine learning versus A.I.
Machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) are related fields, but they are not the same thing. Here's how they differ:
Artificial Intelligence (AI):
AI refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to think and learn like humans. It encompasses a wide range of technologies and techniques that enable machines to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. AI systems can be rule-based or learning-based.
Machine Learning (ML): Machine learning is a subset of AI. It is the process of training a system to learn patterns from data and make predictions or decisions based on that data. In other words, ML algorithms learn from historical data and improve their performance over time without being explicitly programmed. ML is a method used to achieve AI.
Differences:
AI is a broader concept, encompassing anything that allows computers to mimic human intelligence. ML is a specific approach to realizing AI. It focuses on the development of algorithms that allow computers to learn and make predictions or decisions based on data.
Learning:
AI systems can be rule-based, meaning they follow pre-defined rules to make decisions. ML systems learn from data. They improve their performance as they are exposed to more data.
Programming:
AI systems are programmed to follow a set of rules and logic to perform tasks. ML algorithms learn from data and adapt their internal parameters to improve performance. They do not follow strict programming rules but learn from patterns in the data.
Adaptability:
AI systems can be static and may not improve or adapt without manual intervention. ML systems learn and adapt based on new data. The more data they receive, the better they can become at their tasks.
Examples:
AI includes a wide range of applications such as expert systems, speech recognition, and robotics. ML examples include predictive analytics, image recognition, and natural language processing. In essence, machine learning is a technique within the broader field of artificial intelligence. ML enables AI systems to learn and improve their performance by analyzing data, which is a critical aspect of many AI applications. AI, on the other hand, encompasses a wider array of approaches and technologies beyond just machine learning, including expert systems, knowledge representation, and symbolic reasoning.
Never too late to switch to a better CMMS
Start from Scratch or Get Help
Request our technical team to transfer all your current data into Panther CMMS